aircraft category class a b c d
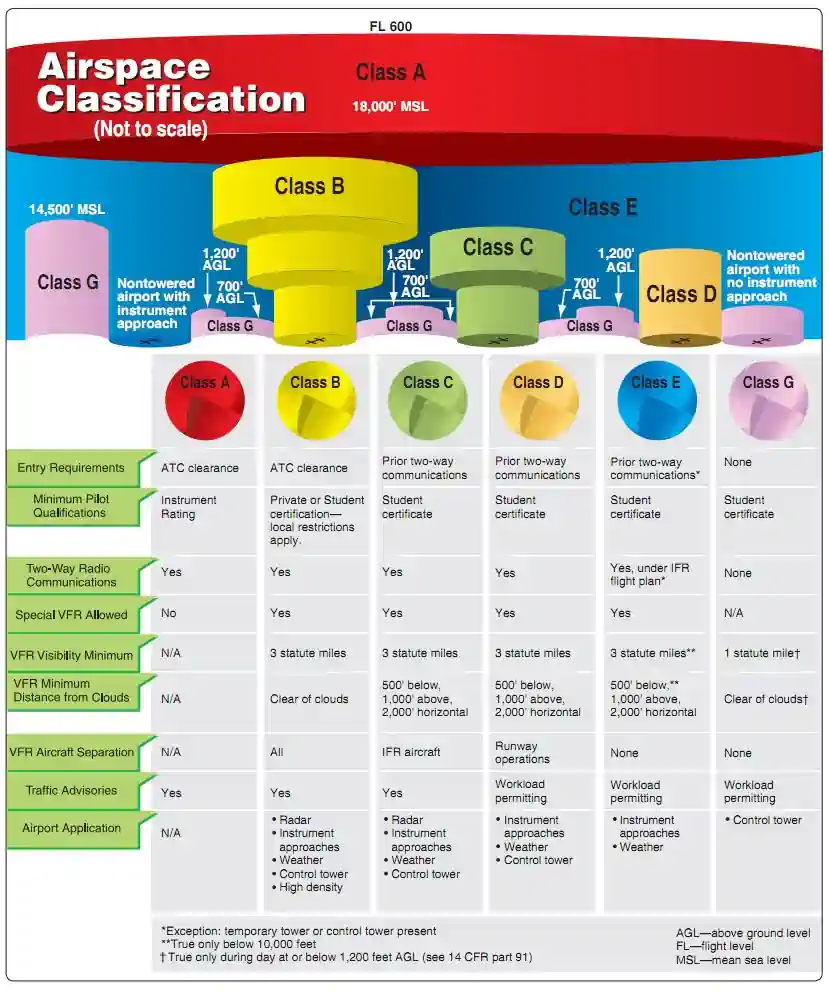
Catagory A Speed less than 91 knots. For example an airplane that fits into Category B but is circling to land at a speed of 145 knots must use the approach Category D minimums.

Icao Aircraft Types And Faa Aircraft Classes Download Table
The Y class is one of the most common and it indicates that you paid full price for an economy seat.
. How to get the right exposure in manual mode. Wild child definition psychology. Indeed chick-fil-a near plovdiv.
Class B is not used. One is to define what size of aircraft the airport has been designed to handle - from something small like an ATR-72 all the way up to the Airbus A380 at the other end of the scale. So lets put the category and classes together with four examples.
The ICAO Aerodrome Reference Code is a two part categorisation of aircraft types which simplifies the process of establishing whether a particular aircraft is able to use a particular aerodrome. Example 1 Cessna 172 Skyhawk Category A. According to the AIM if it becomes necessary to fly faster than the aircrafts published category the minimums for the higher category must be used.
An aircraft shall fit in only one category. The repair interval categories A B C and D listed in column 1 of the MMEL apply only to operations conducted under Parts 121 125 129 and 135. As an additional example a Category A aircraft that is operating at 130 knots on a straight-in approach must use.
This is usually completed as part of your training for a category rating. Speed 166 knots or more. Technically theyre not preformance categories theyre approach categories.
It has two elements the first is a numeric code based on the Reference Field Length for which there are four categories and the seco. Aircraft classifications are useful in airport engineering work including terminal gate sizing apron and taxiway planning etc and in air traffic analyses Most of the airport design standards are related to aircraft size ie wingspan aircraft length. Unless otherwise authorized all pilots must operate their.
Catagory C Speed 121 and less than 141 knots. There are 6 categories -- A Heavy B B757 C Large Jet D Large Commuter E Medium F Small. If it is necessary to maneuver at speeds in excess of the upper limit of a speed range for a category the minimums.
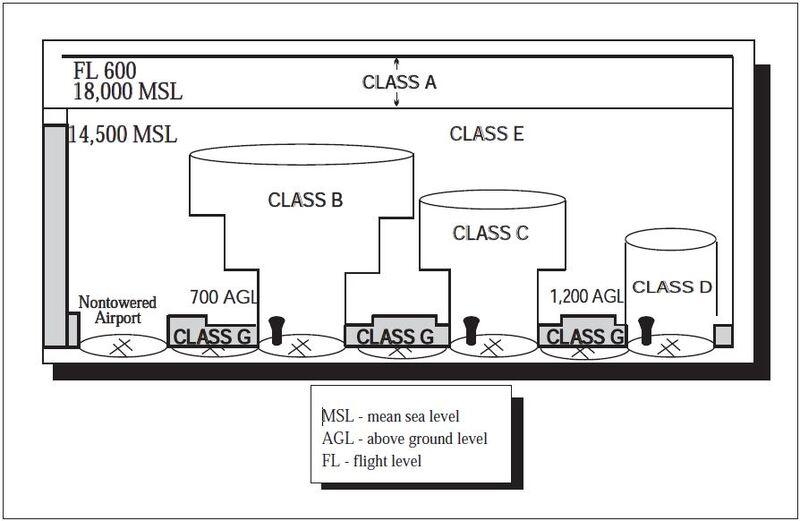
Between 141 knots and 165 knots. Csir net application number lost. Generally airspace from 18000 feet mean sea level MSL up to and including fl ight level FL 600 including the airspace overlying the waters within 12 nautical miles NM of the coast of the 48 contiguous states and Alaska.
Catagory D Speed 141 and less than 166 knots. 141 and less than 166 knots. Between 91 and 120 knots.
VRef VS0 and the maximum certificated landing weight are those values as established for the aircraft by the certification authority of the country of registry. Weight class is based are assigned by APO130 based on the TFMS observed aircraft codes. Class E is generally used for all airspace from 3500 feet to FL195 with the exception of TMAs and airspace over the North Sea.
As is normal in aviation both ICAO and the FAA have their own definitions - the Aerodrome. It has two elements the first is a numeric code based on the Reference Field Length for which there are four categories and the second is letter code. Speed 121 knots or more but less than 141 knots.
All airspace above FL195 is also class C. Specifically the VRef of a given aircraft at the maximum certificated landing weight if VRef is not specified the approach speed is given as the VS0multiplied by 13. Class C is used for busy terminal areas namely Billund TMA and København TMA.
It is included in ICAO Annex 14. Class F is. Between 121 and 140 knots.
Catagory E Speed 166 knots only includes certain military aircraft. Speed 90 knots or less. Repeated solo cross-country flights not more than 50 NM from the point of departure 6193b2 Solo flight in class B airspace 6195a Solo flight to from or at an airport located in Class B 6195a and 91131b2 Complex Airplane Endorsements.
A UH-60 Blackhawk is in the category of rotorcraft and the class of helicopter. We provide more guidance about getting a class rating. Catagory B Speed 91 and less than 121 knots.
No person may act as pilot in command of a complex airplane unless the person has. If you fly the final approach segment at 95 knots indicated you must use Category B minimums. As mentioned earlier some of these codes are universal while others.
Speed 91 knots or more but less than 121 knots. 2 Category B Upper Heavy Aircraft 3 Category C Lower Heavy Aircraft 4 Category D Large Aircraft 5 Category E Small Plus aircraft with a maximum takeoff weight of more than 15400 pounds up to 41000 pounds 6 Category F Small aircraft with a maximum takeoff weight of 15400 pounds or less. Class D is used for all control zones and most terminal areas.
To get a class rating you must complete flight training and pass a flight test with an examiner. When we talk about aircraft categories in relation to the size and maneuverability of the aircraft we are talking about the categories as they are listed under CFR 14. Speed 141 knots or more but less than 166 knots.
Helicopters do not differentiate between multi-engine or single-engine. There are two ways of categorising airports. In the US the maximum speed for determining an approach category is also the maximum speed for maneuvering.
Speed 166 knots or more. Any aircraft weighing more than 255000 lb such as the Boeing 747 or the Airbus A340. A King Air is in the category of airplane and the class of multi-engine land.
The list of Category C airfields in. If the pressure. T is an economy seat that has been discounted J is a business class seat that is full price and D is a business class seat that has been discounted.
For aircraft class rating requirements see Part 61 Division 61L3Aircraft class ratings. The TERPS categories are as follows.

What Is The Difference Between A Category Class And Type Of Aircraft Thinkaviation

Nato Uas Classification 1 2 Download Scientific Diagram
The Airline Pilots Forum And Resource

Protecting Aircraft And Passengers From Cargo Fires Safety First

Types Of Pilot Licenses The Ultimate Guide Thrust Flight

What Is The Difference Between A Category Class And Type Of Aircraft Thinkaviation
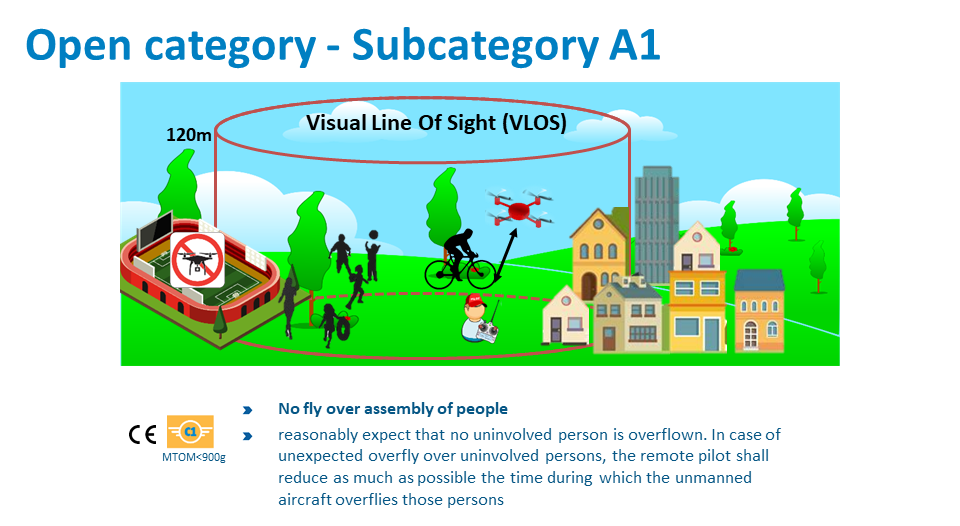
What Are The Requirements Under The Subcategories Of The Open Category Easa

Aircraft Category And Class What Is The Difference Between Them Pilotmall Com

What Are The Different Classes On An Airplane Sheffield
Approach Categories Aviationchief Com
What Is The Difference Between A Category Class And Type Of Aircraft Thinkaviation

What Is The Difference Between A Category Class And Type Of Aircraft Thinkaviation

Faa Aircraft Weight Class And Icao Wake Turbulence Categories Wtc Download Table
What Is The Difference Between A Category Class And Type Of Aircraft Thinkaviation

Airspace Classes Types Of Airspace Classes And How They Are Defined Atp Flight School

What Is The Difference Between A Category Class And Type Of Aircraft Thinkaviation
Enr 1 4 Ats Airspace Classification
What Are The Requirements Under The Subcategories Of The Open Category Easa